RabbitMQ Transport Configuration
The RabbitMQ Transport publishes messages to a RabbitMQ exchange in the eiConsole.
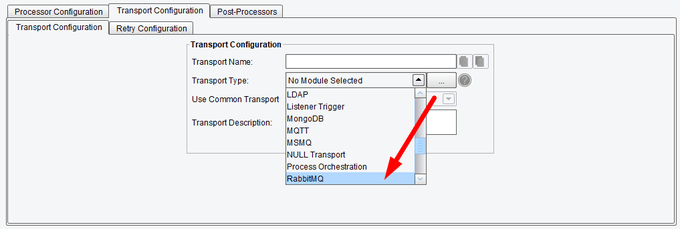
Transport (Adapter) Configuration Drop-Down List
Connection RabbitMQ Transport Configuration Options
On the Connection tab, you can specify:
- Connection Method – the method to use for the connection. The URI method is recommended for single server connections, while Host and Port is recommended for mirrored/HA server setups
- URI – URI of the RabbitMQ Provider (e.g., amqp://localhost)
- Host and Port – specify the host and port for each RabbitMQ Server in the form of host port (e. g., localhost 5672)
- Virtual Host – virtual host to connect to
- Username – the username for the specified server (if required)
- Password – the password for the specified server (if required)
- Use SSL? – check if an SSL connection is required
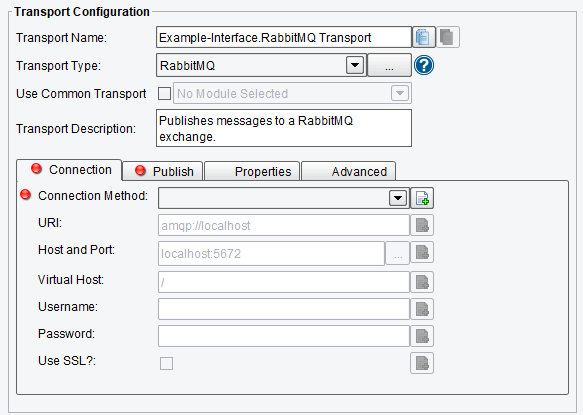
RabbitMQ Transport Connection Configuration Options
Publish RabbitMQ Transport Configuration Options
On the Publish tab, you can specify:
- Routing Key – routing key value for messages
- Exchange – the name of the RabbitMQ Exchange
- Mode – Point-to-Point (Queue) or Publish/Subscribe (Topic) style messaging
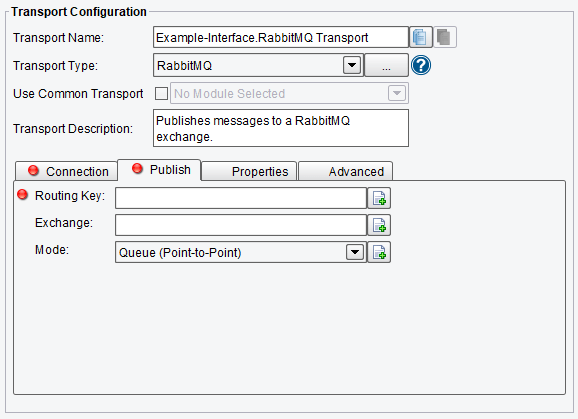
RabbitMQ Transport Publish Configuration Options
Properties RabbitMQ Transport Configuration Options
On the Properties tab, you can specify:
- ContentEncoding – content encoding, e.g. “gzip”. Used by applications, not core RabbitMQ
- ContentType – Content type, e.g. “application/json”. Used by applications, not core RabbitMQ
- CorrelationID – helps correlate requests with responses
- DeliveryMode – 1 or 2. 2 for “persistent”, 1 for “transient”. Some client libraries expose this property as a boolean or enum.
- Expiration – per-message TTL
- MessageID – arbitrary message ID
- Priority – the queue’s priority range should be defined at the time the queue is created. Messages without a set priority default to 0. Messages with a numeric priority higher than the maximum set on the queue will recieve the highest priority the queue supports.
- ReplyTo – response queue name
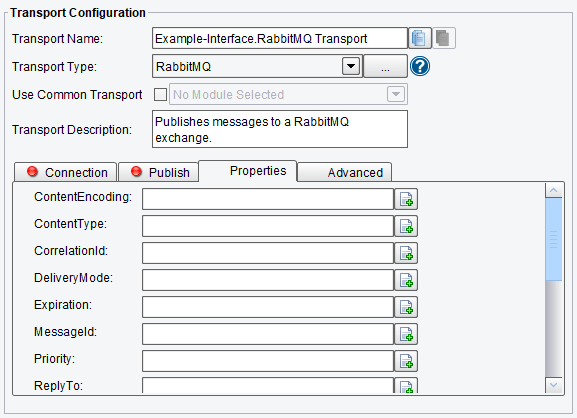
RabbitMQ Transport Properties Configuration Options (top half of screen)
- Timestamp – an application-provided timestamp
- Type – application-specific message type, e.g. “orders.created”
- UserID – user ID, validated if set
- AppID – application name
- Headers – an arbitrary map of headers with string header names
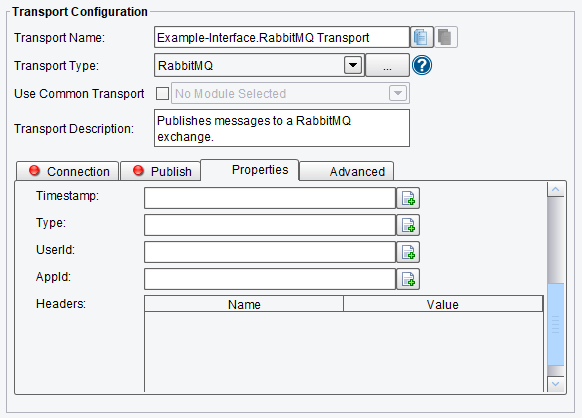
RabbitMQ Transport Properties Configuration Options (bottom half of screen)
Advanced RabbitMQ Transport Configuration Options
On the Advanced tab, you can specify:
- Synchronous Acknowledge – if enabled, message acknowledgment will be sent by the Listener after the message is delivered by this Transport
- Declare – create the queue or exchange if it does not already exist
- Durable – are messages durable (survive RabbitMQ server restart)
- Exclusive – the queue is exclusive to this connection
- Auto-Delete – queue deleted when not in use
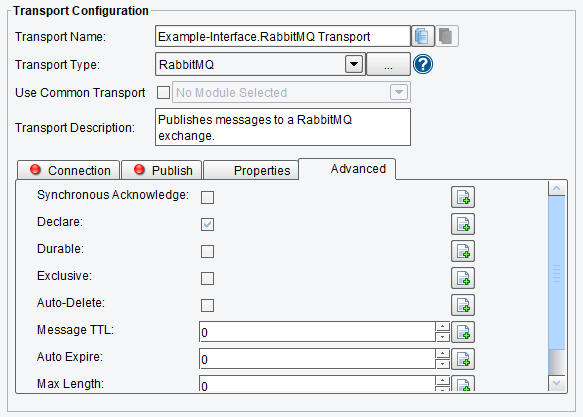
RabbitMQ Transport Advanced Configuration Options (top half of screen)
- Message TTL – how long a message published to a queue can live before it is discarded (milliseconds)
- Auto Expire – how long a queue can be unused before it is automatically deleted (milliseconds)
- Max Length – how long a queue can be unused before it is automatically deleted (milliseconds)
- Dead Letter Exchange – the name of the exchange to send rejected messages to (must be set at time queue is created)
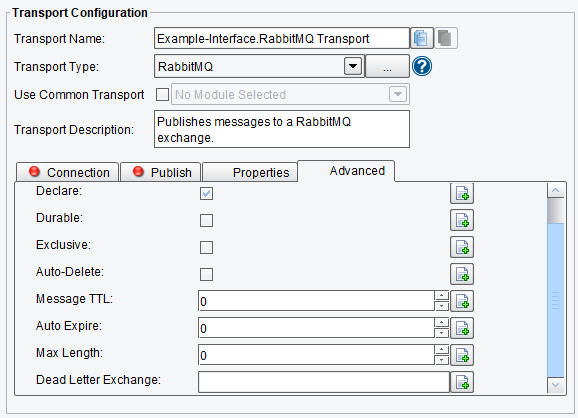
RabbitMQ Transport Advanced Configuration Options (bottom half of screen)
If you’re curious about the software features, free trial, or even a demo – we’re ready to answer any and all questions. Please call us at 813 864 8662 or click the button.
